Topos Explorer
You have tried the ERC20 Messaging dApp to see Topos in action and have executed a cross-subnet token transfer. You were presented with a very high-level view of what happened, just like what a user would see.
You can now use the Topos Explorer to see more details. Because Topos subnets are EVM-based, an explorer for Topos can use the usual exposed Ethereum JSON-RPC API. In addition, the Transmission Control Engine (TCE) will expose a GraphQL endpoint.
Navigate to the Topos Explorer:
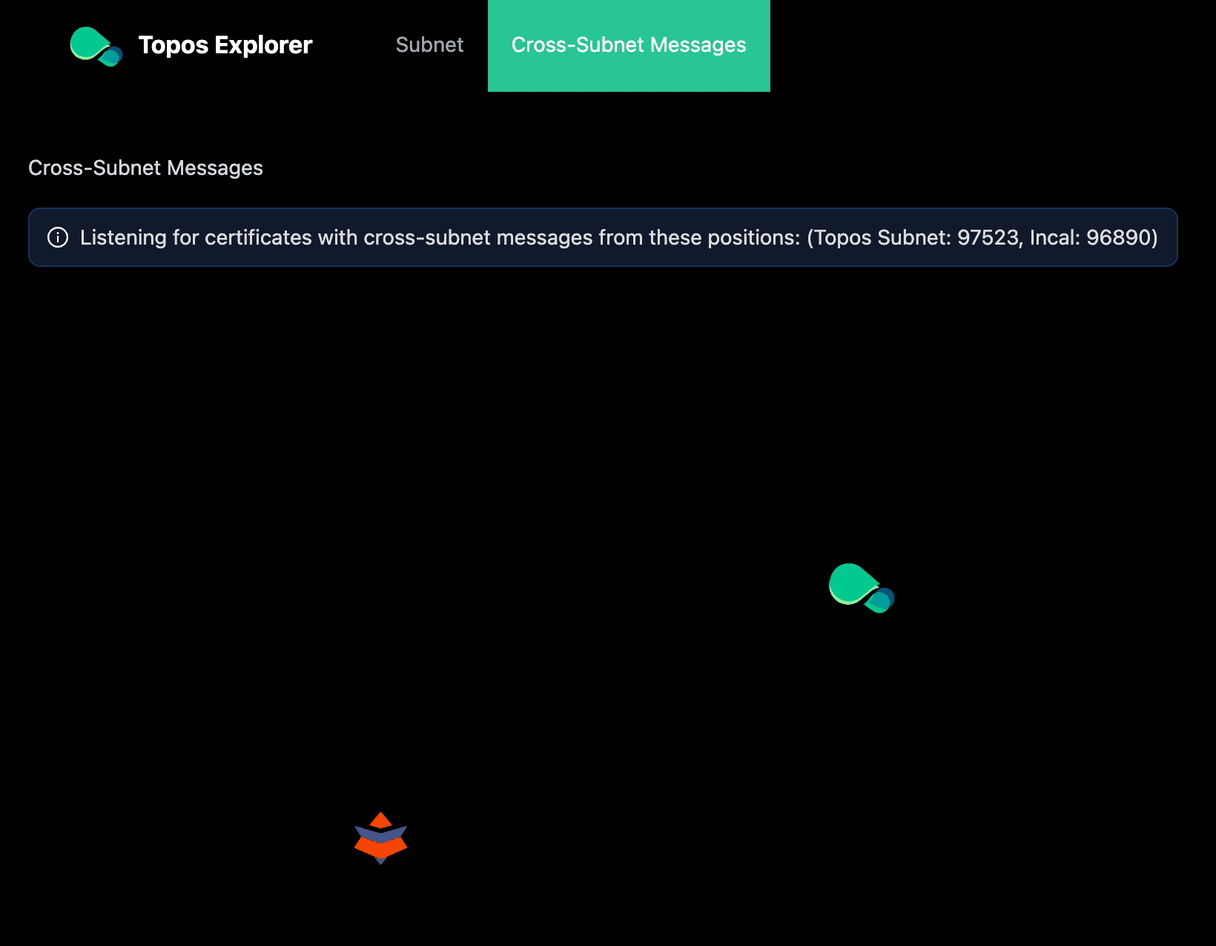
If you look at the Topos Subnet by clicking on the Subnet tab, you will observe multiple pieces of information about the subnet:
- Subnet name
- Subnet ID
- Subnet currency
- Subnet RPC endpoint
- Latest blocks being created
- Latest certificates being created
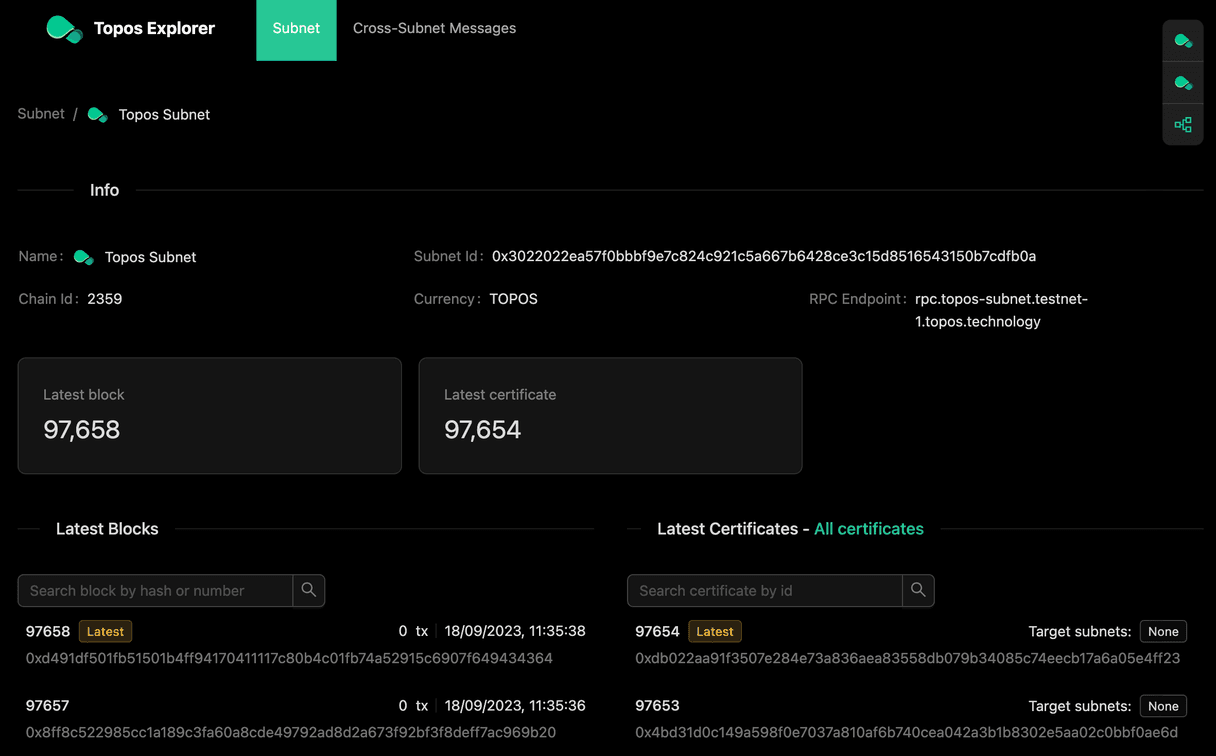
The Explorer catches live data in the moment without an indexer running in the background. Nevertheless you can find a link to all certificates above the latest certificates or search old blocks and certificates.
During your tests with the Playground, you created some transactions. Look for the blocks including these transactions:
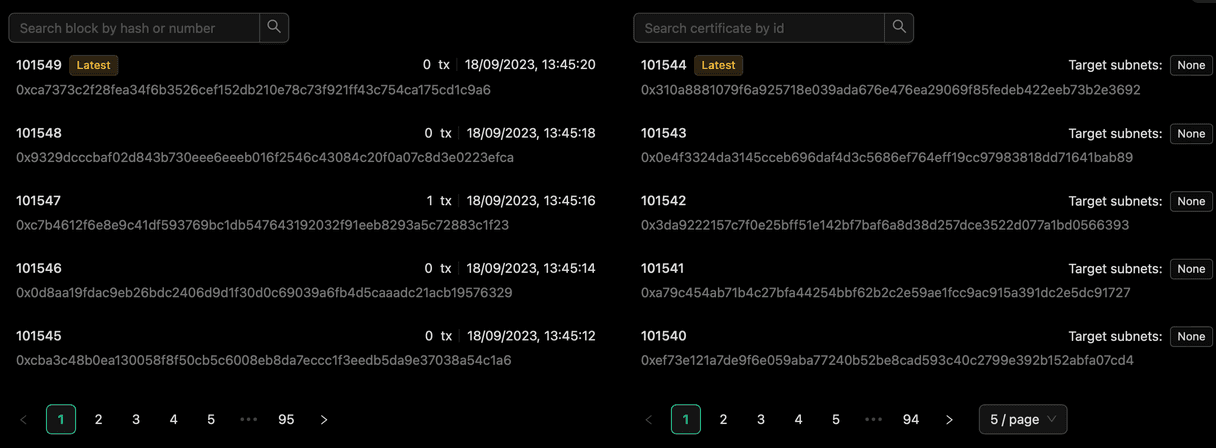
You can see further details by clicking on a block:
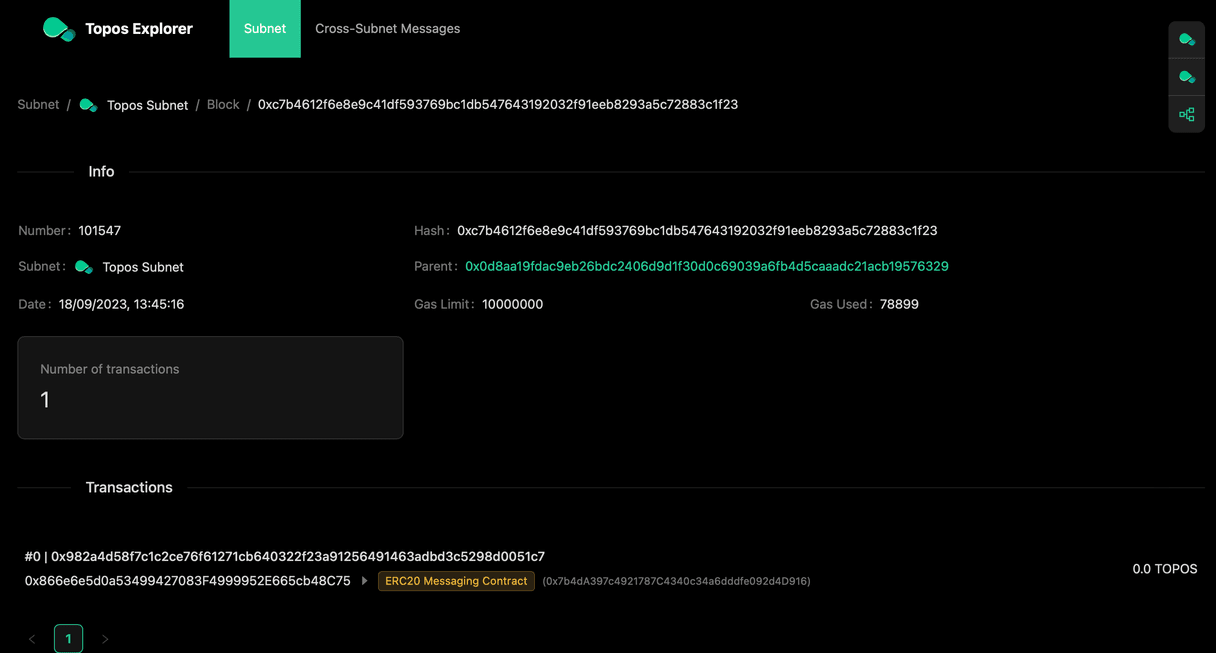
Here you can see that the cross-subnet token transfer you invoked triggered a call on the ERC20 Messaging Contract.
You learned about the ERC20Messaging contract in the first chapter. This optional contract is used in the context of the ERC20 Messaging dApp for cross-subnet token transfers.
Topos guarantees that certificates are delivered with certain conditions fulfilled, like causal ordering. The execution logic of the transactions included in those certificates is not part of the core protocol. The Topos executor service on the other hand is an example implementation for such a logic. You can call the executor service API endpoint in your browser in order to receive further information. Note that you will need to authenticate your request.
Up next
It is nice to have these kinds of tools to get started with a new protocol. Of course, a lot of details remain hidden. The next section will explain how to run a local network and examine the actions that took place during your test.